描述
ASTM Seamless Pipe
ASTM Standards can be purchased as a digital library subscription or individually from ASTM and other qualified standards providers.
Our ASTM Specification pipe and tube are locally sourced, developed and produced which means our customers are assured of the highest quality standards and a local, concerned customer service presence invested in the success of your project We manufacture our tubular products at several Chinese based facilities that produce high-quality tubular products with low-residuals in a wide range of strength levels with superior toughness.
ASTM Standards for steel pipes
ASTM’s steel standards are instrumental in classifying, evaluating, and specifying the material, chemical, mechanical, and metallurgical properties of the different types of steels, which are primarily used in the production of mechanical components, industrial parts, and construction elements, as well as other accessories related to them.
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders, masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
These steel standards are helpful in guiding metallurgical laboratories and refineries, product manufacturers, and other end-users of steel and its variants in their proper processing and application procedures to ensure quality towards safe use.
ASTM standards for Steel pipes
| Abbr. | Corresponding | Application |
| A53 | ASTM A53/A53m-99b | specification for pipe, steel, black and hot-dipped, zinc-coated, welded and seamless |
| A74 | ASTM A74-98 | specification for cast iron soil pipe and fittings |
| A106 | ASTM A106-99e1 | specification for seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service |
| A126 | ASTM A126-95e1 | specification for grey iron castings for valves, flanges, and pipe fittings |
| A134 | ASTM A134-96 | specification for pipe, steel, electric-fusion (arc)-welded (sizes nps 16 and over |
| A135 | ASTM A135-97c | specification for electric-resistance-welded steel pipe |
| A139 | ASTM A139-96e1 | specification for electric-fusion (arc)-welded steel pipe (nps 4 and over) |
| A182 | ASTM A182/A182m-99 | specificationfor forged or rolled alloy-steel pipe flanges, forged fittings, and valves and parts for high-temperature service |
| A252 | ASTM A252-98 | specification for welded and seamless steel pipe piles |
| A312 | ASTM A312/a312m-00 | specification for seamless and welded austenitic stainless steel pipes |
| A333 | ASTM A333/A333m-99 | specification for seamless and welded steel pipe for low-temperature service |
| A335 | ASTM A335/A335m-99 | specification for seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe for high-temperature service |
| A338 | ASTM A338-84(1998) | specificationfor malleable iron flanges, pipe fittings, and valve parts for railroad, marine, and other heavy duty service at temperatures up to 650°f (345°c) |
| A358 | ASTM A358/A358m-98 | specification for electric-fusion-welded austenitic chromium-nickel alloy steel pipe for high-temperature service |
| A369 | ASTM A369/A369m-92 | specification for carbon and ferritic alloy steel forged and bored pipe for high-temperature service |
| A376 | A376/A376m-98 | specification for seamless austenitic steel pipe for high-temperature central-station service |
| A377 | ASTM A377-99 | index of specifications for ductile-iron pressure pipe |
| A409 | ASTM A409/A409m-95ae1 | specification for welded large diameter austenitic steel pipe for corrosive or high-temperature service |
| A426 | ASTM A426-92(1997) | specification for centrifugally cast ferritic alloy steel pipe for high-temperature service |
| A451 | ASTM A451-93(1997) | specification for centrifugally cast austenitic steel pipe for high-temperature service |
| A523 | ASTM A523-96 | specification for plain end seamless and electric-resistance-welded steel pipe for high-pressure pipe-type cable circuits |
| A524 | ASTM A524-96 | specification for seamless carbon steel pipe for atmospheric and lower temperatures |
| A530 | ASTM A530/A530m-99 | specification for general requirements for specialized carbon and alloy steel pipe |
| A648 | ASTM A648-95e1 | specification for steel wire, hard drawn for prestressing concrete pipe |
| A674 | ASTM A674-95 | practice for polyethylene encasement for ductile iron pipe for water or other liquids |
| A691 | ASTM A691-98 | specification for carbon and alloy steel pipe, electric-fusion-welded for high-pressure service at high temperatures |
| A694 | ASTM A694/A694m-00 | specification for carbon and alloy steel forgings for pipe flanges, fittings, valves, and parts for high-pressure transmission service |
| A716 | ASTM A716-99 | specification for ductile iron culvert pipe |
| A733 | ASTM A733-99 | specification for welded and seamless carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel pipe nipples |
| A742 | ASTM A742/A742m-98 | specification for steel sheet, metallic coated and polymer precoated for corrugated steel pipe |
| A746 | ASTM A746-99 | specification for ductile iron gravity sewer pipe |
| A760 | ASTM A760/A760m-99 | specification for corrugated steel pipe, metallic-coated for sewers and drains |
| a761 | ASTM A761/A761m-98 | specification for corrugated steel structural plate, zinc-coated, for field-bolted pipe, pipe-arches, and arches |
| A762 | ASTM A762/A762m-98 | specification for corrugated steel pipe, polymer precoated for sewers and drains |
| A790 | ASTM A790/A790m-99 | specification for seamless and welded ferritic/austenitic stainless steel pipe |
| A796 | ASTM A796/A796m-99 | practice for structural design of corrugated steel pipe, pipe-arches, and arches for storm and sanitary sewers and other buried applications |
| A798 | ASTM A798/A798m-97a | practice for installing factory-made corrugated steel pipe for sewers and other applications |
| A807 | ASTM A807/A807m-97 | practice for installing corrugated steel structural plate pipe for sewers and other applications |
| A810 | ASTM A810-94 | specification for zinc-coated (galvanized) steel pipe winding mesh |
| A813 | ASTM A813/A813m-95e2 | specification for single- or double-welded austenitic stainless steel pipe |
| A814 | ASTM A814/A814m-96 (1998) | specification for cold-worked welded austenitic stainless steel pipe |
| A849 | ASTM A849-99 | specification for post-applied coatings, pavings, and linings for corrugated steel sewer and drainage pipe |
| A861 | ASTM A861-94e1 | specification for high-silicon iron pipe and fittings |
| A862 | ASTM A862/A862m-98 | practice for application of asphalt coatings to corrugated steel sewer and drainage pipe |
| A865 | ASTM A865-97 | specification for threaded couplings, steel, black or zinc-coated (galvanized) welded or seamless, for use in steel pipe joints |
| A872 | ASTM A872-91 (1997) | specification for centrifugally cast ferritic/austenitic stainless steel pipe for corrosive environments |
| A885 | ASTM A885/A885m-96 | specification for steel sheet, zinc and aramid fiber composite coated for corrugated steel sewer, culvert, and underdrain pipe |
| A888 | ASTM A888-98e1 | specification for hubless cast iron soil pipe and fittings for sanitary and storm drain, waste, and vent piping applications |
| A926 | ASTM A926-97 | test method for comparing the abrasion resistance of coating materials for corrugated metal pipe |
| A928 | ASTM A928/A928m-98 | specification for ferritic/austenitic (duplex) stainless steel pipe electric fusion welded with addition of filler metal |
| A929 | ASTM A929/A929m-97 | specification for steel sheet, metallic-coated by the hot-dip process for corrugated steel pipe |
| A930 | ASTM A930-99 | practice for life-cycle cost analysis of corrugated metal pipe used for culverts, storm sewers, and other buried conduits |
| A943 | ASTM A943/A943m-95e1 | specification for spray-formed seamless austenitic stainless steel pipes |
| A949 | ASTM A949/A949m-95e1 | specification for spray-formed seamless ferritic/austenitic stainless steel pipe |
| A954 | ASTM A954-96 | specification for austenitic chromium-nickel-silicon alloy steel seamless and welded pipe |
| A972 | ASTM A972/A972m-99 | specification for fusion bonded epoxy-coated pipe piles |
| A978 | ASTM A978/A978m-97 | specification for composite ribbed steel pipe, precoated and polyethylene lined for gravity flow sanitary sewers, storm sewers, and other special applications |
| A984 | ASTM A984/A984m-00 | specification for steel line pipe, black, plain-end, electric-resistance-welded |
| A998 | ASTM A998/A998m-98 | practice for structural design of reinforcements for fittings in factory-made corrugated steel pipe for sewers and other applications |
| A999 | A999/A999m-98 | specification for general requirements for alloy and stainless steel pipe |
| A1005 | ASTM A1005/A1005m-00 | specification for steel line pipe, black, plain end, longitudinal and helical seam, double submerged-arc welded |
| A1006 | ASTM A1006/A1006m | specification for steel line pipe, black, plain end, laser beam welded |
ASTM standards for Heat-exchanger and condenser tubes
| Abbr. | Corresponding | Application |
| A179 | ASTM A179 / A179M | Standard Specification for Seamless Cold-Drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes |
| A213 | ASTM A213/A213M | Specification for Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy-Steel Boiler, Superheater, and Heat-Exchanger Tubes |
| A214 | ASTM A214 / A214M | Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes |
| A249 | ASTM A249 / A249M | Specification for Welded Austenitic Steel Boiler, Superheater, Heat-Exchanger, and Condenser Tubes |
| A498 | ASTM A498 / A498M | Specification for Seamless and Welded Carbon, Ferritic, and Austenitic Alloy Steel Heat-Exchanger Tubes with Integral Fins |
| A851 | ASTM A851 / ASME SA851 | Specification for High-Frequency Induction Welded, Unannealed, Austenitic Steel Condenser Tubes |
ASTM standards for Mechanical tubing
| Abbr. | Corresponding | Application |
| A511 | ASTM A511 / A511M | Specification for Seamless Stainless Steel Mechanical Tubing |
| A512 | ASTM A512 / ASME SA512 | Specification for Cold-Drawn Buttweld Carbon Steel Mechanical Tubing |
| A513 | ASTM A513 / A513M | Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon and Alloy Steel Mechanical Tubing |
| A519 | ASTM A519 / A519M | Specification for Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel Mechanical Tubing |
| A554 | ASTM A554 | Specification for Welded Stainless Steel Mechanical Tubing |
ASTM standards for Structural tubing
| Abbr. | Corresponding | Application |
| A500 | ASTM A500 / A500M | Specification for Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and Shapes |
| A501 | ASTM A501 / A501M | Specification for Hot-Formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing |
| A847 | ASTM A847 / A847M | Specification for Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless High Strength, Low Alloy Structural Tubing with Improved Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance |
| A618 | ASTM A618 / A618M | Specification for Hot-Formed Welded and Seamless High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing |
ASTM standards for Welding fittings
| Abbr. | Corresponding | Application |
| A234 | ASTM A234 / A234M | Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and High Temperature Service |
| A403 | ASTM A403/A403M | Specification for Wrought Austenitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittings |
| A420 | ASTM A420 / A420M | Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Low-Temperature Service |
| A774 | ASTM A774 / A774M | Specification for As-Welded Wrought Austenitic Stainless Steel Fittings for General Corrosive Service at Low and Moderate Temperatures |
| A758 | ASTM A758 / A758M | Specification for Wrought-Carbon Steel Butt-Welding Piping Fittings with Improved Notch Toughness |
Conversion from ASTM Standards
Engineering specification is also a language, and standard specifications for material and processes are defined differently in each country in the world. To a new designer, steel grades might seem easy, where 316 stainless steel is one material and cast iron another, but there are variations in each of these categories of metal. Rumors abound about people receiving poor quality steels from other jurisdictions. It leaves some designers wondering if there is something intrinsic in the official standards in other countries that can lead to these complaints.
International standards do not translate, metal-for-metal, the way words might translate. When converting from one standard to another, it’s almost impossible to find identical compositions for a given type of metal. The question becomes: can you find an equivalent? This can be confusing, as each named metal grade has its own chemistry and production guidelines.
For people without a materials background, these differences can make the purchase of foreign-made metal seem iffy, like ordering an inferior knockoff. However, the quality of the grades of steel are as good, country to country. Understanding what makes a steel standard or specification can help a North American business navigate overseas production.
Steel grades explained
Metal alloys are a mixture of different proportions of elements. A standard includes the chemistry, or “recipe” for the alloy, documenting what different elements should be melted into it. Specific instructions may also be given on melting temperature, cooling, and treatment.
Published standards also record the mechanical properties of a specified metal. If it has been made correctly, a metal should not only have the correct chemical analysis, but also perform within the correct range in mechanical tests.
Steels contain iron and carbon. Standards for each grade of steel specify the proportions by weight of each of these elements, as well as any additional elements alloyed with them. These additions may create different characteristics: for example, chromium is present in stainless steel to help prevent rusting.
In most consumer metal standards, the proportions of each element are given an acceptable range, rather than a precise number. For example, the ASTM 1050 grade steel is so named because it is approximately .50% carbon by weight. However, the tolerance for carbon percentage in the ASTM 1050 standard is .48-.55%. A similar Japanese specification sets carbon between .47-.53%, and allows for silicon and other trace elements, whereas the ASTM standard does not.
Steel specifications often provide ranges for carbon, manganese, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, and none set identical ranges for each element. It is for this reason that steel standards from different organizations are not precise matches: the tolerances merely overlap. If one steel specifies less than .007% sulfur content, and another allows up to .040%, are they different steels? Small changes do not matter in many situations but may be relevant depending on the metal’s intended use.
It is not just chemistry, but also processing, that changes the behavior of a metal. Metal is crystalline and forms grain microstructures as it cools. Chemistry, melting, cooling, and heat treatment all can change the grain of the metal. This directly influences tensile strength, hardness, and brittleness. Therefore, steel specification may also include the production steps needed to create particular microstructures, including martensite, austenite, or ferrite grains.
When making a substitution between one standard and another, a skilled metallurgist or engineer will evaluate comparable grades based on mechanical properties. The engineer considers what the final product needs to do, and in what conditions. Using their understanding of chemistry, the expected working load, and knowledge of the conditions the product will work in, they can find a steel for the product’s requirements in any standard. All recognized steel standards generally have equivalent rigor, making this translation possible.
It is not a difference in published standards that are the source of poor-quality foreign metals.
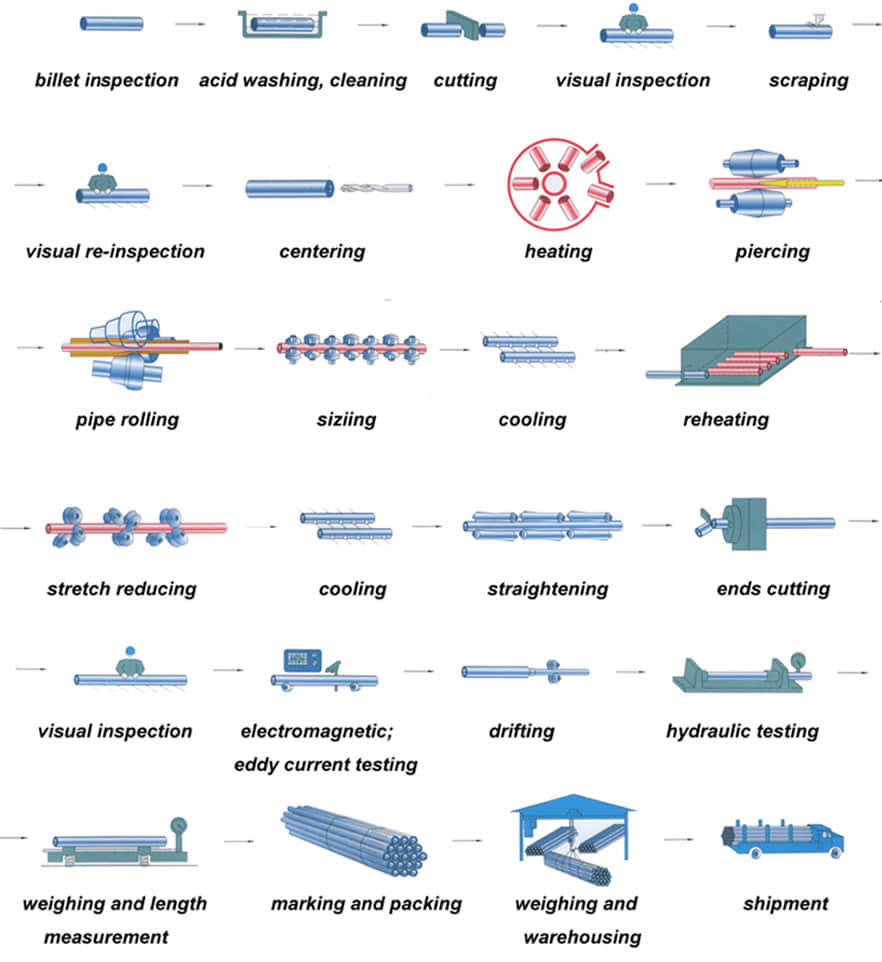
Process
Cold drawn seamless steel tube deformed process
Cold Drawn Seamless Mechanical Tubing (CDS) is a cold drawn 1018/1026 steel tube which offers uniform tolerances, enhanced machinability and increased strength and tolerances compared to hot-rolled products.
Cold drawn steel tube is with hot-rolled steel coil as raw material, and tandem cold rolling pickled to remove oxide scale, its finished rolling hard roll, rolling hard volumes due to the continuous cold deformation caused by cold hardening strength, hardness increased indicators declined tough plastic, stamping performance will deteriorate, which can only be used for simple deformation of the parts.
Rolling hard roll can be used as the raw material of the hot-dip galvanizing plant, hot dip galvanizing line set annealing line. Rolling hard roll weight is generally 6 to 13.5 tons, the coil diameter of 610mm.
Hot rolled seamless steel pipe deformed process
Hot-rolled seamless steel pipe production base deformation process can be summarized as three stages: perforation, extension and finishing.
The main purpose of the perforation process is to become a solid round billet piercing hollow shell. Capillary in the specifications, accuracy and surface quality can not meet the requirements of the finished product, further improvements are needed to deform the metal through. The main purpose of the stretching machine is further reduced sectional view (main compression wall) for a larger axial extension, so that the capillary improved dimensional accuracy, surface quality and organizational performance.
After stretching machine rolled steel pipe shortage collectively need further molding mill in order to achieve the requirements of the finished pipe. Rolled steel due to pass in the method widely used in the production of seamless steel tubes.
So far, due to the method pass rolling steel can be divided into two categories: core pension without rolling rolling (hollow body rolling), and with the mandrel. Sizing machines, reducing mill and stretch reducing mill belonging to the hole without mandrel type continuous rolling mills are generally coffin. Its main purpose is to reduce the diameter of the deformation process or sizing get finished steel, the wall thickness of process control, can make thinning, thickening or nearly unchanged.
All the traditional hole-type rolling machine with mandrel belong to extend machine. The main purpose is to reduce the deformation process perforated capillary wall thickness and outer diameter roll passes in the deformation zone and the mandrel posed, for a larger axial extension. At the same time a certain improvement in the organization, performance, accuracy, surface quality.
Carbon steel seamless pipes
The complex chemical and physical properties of the various grades of carbon steel pipe allow for a broad range of service usage.
American Piping Products has the right grade, size and price to meet your requirements, including A/SA-106 Grade B/C and API 5L X- 42 thru X -70. A/SA-106 Grades B & C are utilized for services ranging from structural supports to steam drum headers with temperature ranges up to 800°F, while API 5L X Grades 42 thru 70 are utilized for the water and petroleum industry to transport liquids or as platforms on off-shore rigs.
Available grades and size range
Carbon steel is an alloy with carbon and iron, with carbon content up to 2.1% by weight. The increase in the carbon percentage will raise steel’s hardness and strength, but it will be less ductile. Carbon steel has good properties in hardness and strength, and it is less expensive than other steels.
API SPEC 5CT
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
| Casting | API 5CT | Ø114~219 x WT5.2~22.2 | J55, K55, N80, L80, P110 |
| Tubing | API 5CT | Ø48.3~114.3 x WT3.2~16 | J55, K55, N80, L80, P110 |
API SPEC 5L
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
| Line Pipes | API 5L | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~120 | A, B, X42, X46, X52, X60, X70, X80, PSL1 / PSL2 |
ASTM / ASME
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
| Black and Hot-Dipped Zinc-Coated Seamless Steel Pipes | ASTM A53 | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~150 | Gr.A, Gr.B, Gr.C |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Pipes for High Temperature Service | ASTM A106 | Ø10.3~1200 x WT1.0~150 | Gr.B, Gr.C |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A179 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Boiler Tubes for High Pressure | ASTM A192 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Intermediate Alloy Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A199 | Ø10.3~426 x 1.0~36 | T5, T22 |
| Seamless Medium-Carbon Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes | ASTM A210 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | A1, C |
| Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy Steel Boiler, Superheater and Heat-Exchanger Tubes | ASTM A213 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | T5, T9, T11, T12, T22, T91 |
| Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel for Mechanical Tubing | ASTM A333 | Ø1/4″~42″ x WT SCH20~XXS | Gr.1, Gr.3, Gr.6 |
| Seamless and Welded Carbon Steel Pipes and Alloy Steel Pipes for Low Temperature Use | ASTM A334 | Ø1/4″~4″ x WT SCH20~SCH80 | Gr.1, Gr.6 |
| Seamless Cold-Drawn Carbon Steel Feedwater Heater Tubes | ASTM A556 | Ø10.3~426 x WT1.0~36 | A2, B2 |
DIN
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Elevated Temperature | DIN 17175 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | St35.8, St45.8, 10CrMo910, 15Mo3, 13CrMo44, STPL340, STB410, STB510, WB36 |
| Seamless Steel Tubes | DIN 1629 / DIN 2391 | Ø13.5~762 x WT1.8~120 | St37.0, St44.0, St52.0, St52.3 |
| Seamless Steel Tubes | DIN 2440 | Ø13.5~165.1 x WT1.8~4.85 | St33.2 |
| Seamless Steel Pipes for Structural Purpose | DIN 2393 | Ø16~426 x WT1.0~36 | RSt34-2, RSt37-2, RSt44-2, St52 |
BS
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Machine Structure | BS 970 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Steel Tubes for Boiler and Heat Exchangers | BS 3059 | Ø10~762 x WT1.0~120 | 360, 410, 440, 460, 490 |
Application
Carbon steel seamless pipes are extensively applied in the nuclear device, gas conveyance, petrochemical, shipbuilding and boiler industries, with characteristics of high corrosion resistance combined with suitable mechanical properties.
– Nuclear device
– Gas conveyance
– Petrochemical industries
– Shipbuilding and boiler industries
European Standards for steel
With so many European Standards specifying steel and steel products and replacing national standards, it is necessary to have a European designation system for steel.
Such a system is well established and implemented in almost all the European Standards. European Standards for steel products are the responsibility of the European Committee for Iron and Steel Standardization.
ECISS has the task of developing European Standards for the definition, classification, testing, analysis and technical delivery requirements for the products of the iron and steel industry and the implementation of these as national standards by members in order to achieve technical harmonization within the European Union. ECISS is an Associated Standards Body within the framework of the European Committee of Standardization.
European Standards published in the UK have the status of a British Standard and are characterized by the prefix ‘BS EN’ to their reference number. Other national standards bodies of Member States of the European Union publish identical European Standards with their appropriate prefixes, e.g. in Germany, ‘DIN EN’, in France ‘NF EN’, in Sweden ‘SIS EN’ etc. European Standards are essentially voluntary instruments except for certain situations, e.g. Public Procurement Directives, Construction Products Directive. According to the CEN rules, members in the UK, that is BSI, are obliged to announce the availability of European Standards and publish the identical text and to withdraw any conflicting national standards.
BS3059 II 360
BS 3059-2:1990 requirements for tubes not exceeding 127 mm outside diameter and 12.5 mm thickness. Depending on the operating temperature, it can be divided into two kinds general boiler pipes and high-pressure boiler pipes.
BS3059-II 440
BS 3059 PART 2-78 is the standard specifies the steel boiler and superheter tubes carbonn alloy and specified elevated temperature prop.
EN10216-1
P235GH is a European specified steel for use in pressure vessels, boilers and heat exchangers. The composition of this steel makes it ideal for applications where elevated working temperatures are the norm and the material is used by fabricators throughout the oil, gas and petrochemical industry.
Seamless steel tubes for pressure purposes
- EN 10216-1 Non-alloy steel tubes with specified room temperature properties
- EN 10216-2 Non alloy and alloy steel tubes with specified elevated temperature properties
- EN 10216-3 Alloy fine grain steel tubes
- EN 10216-4 Non-alloy and alloy steel tubes with specified low temperature properties
- EN 10216-5 Stainless steel tubes
Material
- z.Bsp: P235GH TC1, P235GH TC2, 16Mo3
DIN 17175
DIN 17175 steel pipes are used in boiler installations, high-pressure pipelines and tank construction and special machinery for both high (градусов 600) temperature and high-pressure devices. This alloy steel pipe is just a big class,and it has many classifivations.
EN 10028 – P265GH
P265GH is a weldable pressure vessel and boiler steel grade used by the world’s industrial fabricators. The material, which is ideally suited for elevated temperature service, is commonly found in the oil & gas, petrochemical and chemical industry.
DIN 2391
DIN 2391 standard specifies the Seamless steel tubes used forMechanical and Automobile.
BSP British Standard Pipe
The British Standard Pipe (BSP) is a family of standard screw thread types that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipe ends by mating an external (male) with an internal (female) thread.
BS3059 Part I, BS3059-I 320 CFS
BS 3059 standard accord to the steel boiler and superheater tubes. Part I-87 low tensile carbon steel tube without specified elevated temperature preperites.
DIN 2440
The DIN 2440 standard applies to medium-weight tubes suitable for screwing used in applications of medium pressure air and non-hazardous gases. The most common material is St33.2(also known as S185) conforming to DIN 17100. DIN 2440 steel pipes are often supplied in seamless type with zinc coating.
Old and new DIN Designations
Over the years, many DIN standards were integrated into the ISO standards, and thus also a part of the EN standards. In the cource of the revision of the European standards serveral DIN standards were withdrawn and replaced by DIN ISO EN and DIN EN.
The standards used in the past such as the DIN 17121, DIN 1629, DIN 2448 and the DIN 17175 have since been mostly replaced by Euronorms. The Euronorms clearly distinguish the pipe’s area of application. Consequently different standards now exist for pipes used as construction materials, pipelines or for mechanical engineering applications.
This distinction was not as clear in the past. For example, the old St.52.0 quality was derived from the DIN 1629 standard which was intended for pipeline systems and mechanical engineering applications. This quality was also often used for steel structures, however.
The info below explains the main standards and steel qualities under the new system of standards.
Seamless Pipes and Tubes for Pressure Applications
The EN 10216 Euronorm replaces the old DIN 17175 and 1629 standards. This standard is designed for pipes used in pressure applications, such as a pipeline. This is why the associated steel qualities are designated by the letter P for ‘Pressure’. The value that follows this letter designates the minimum yield strength. The subsequent letter designations provide additional information.
The EN 10216 comprises several parts. The parts that are relevant to us are as follows:
- EN 10216 Part 1: non-alloy pipes with specified properties at room temperature
- EN 10216 Part 2: non-alloy pipes with specified properties at higher temperatures
- EN 10216 Part 3: alloy pipes made from fine-grained steel for any temperature
Some examples:
- EN 10216-1, Quality P235TR2 (formerly DIN 1629, St.37.0)
P = Pressure
235 = minimum yield strength in N/mm2
TR2 = quality with specified properties relating to aluminum content, impact values and inspection and test requirements. (In contrast to TR1, for which this is not specified). - EN 10216-2, Quality P235 GH (formerly DIN 17175, St.35.8 Cl. 1, boiler pipe)
P = Pressure
235 = minimum yield strength in N/mm2
GH = tested properties at higher temperatures - EN 10216-3, Quality P355 N (more or less equivalent to DIN 1629, St.52.0) P = Pressure
355 = minimum yield strength in N/mm2
N = normalized*
* Normalized is defined as: normalized (warm) rolled or standard annealing (at a min temperature of 930°C). This applies to allqualities designated by the letter ‘N’ in the new Euro Standards.
Pipes: the following standards are replaced by DIN EN
Old standard
| Execution | Norm | Steel grade |
| Welded | DIN 1626 | St.37.0 |
| Welded | DIN 1626 | St.52.2 |
| Seamless | DIN 1629 | St.37.0 |
| Seamless | DIN 1629 | St.52.2 |
| Seamless | DIN 17175 | St.35.8/1 |
| Seamless | ASTM A106* | Grade B |
| Seamless | ASTM A333* | Grade 6 |
New standard
| Execution | Norm | Steel grade |
| Welded | DIN EN 10217-1 | P235TR2 |
| Welded | DIN EN 10217-3 | P355N |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-1 | P235TR2 |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-3 | P355N |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-2 | P235GH |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-2 | P265GH |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-4 | P265NL |
* ASTM standards will remain valid and will not be replaced by Euronorms in the near future













评价
目前还没有评价